Question:
What are the magnitudes of the pulling force and the magnetic field
Answer:
The magnetic field strength is 2.7 T
The pulling force
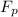 is 0.975 N
is 0.975 N
Step-by-step explanation:
Here we have;
Length of wire, l = 10.0 cm = 0.1 m
Resistance of wire, R = 0.300 Ω
Speed of wire, v = 4.00 m/s
Power dissipated = 3.90 W
Based on the given data, we apply the relation;
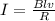 ..............(1)
..............(1)
Where:
B = Magnetic field strength
I = Current
Since P = I²R, we have;
3.9 = I²·0.300Ω
∴ I² = 3.9/0.300 = 13
From which I = √13
Substituting the value of I in equation (1) above, we have;
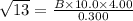
Therefore;
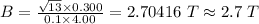
The magnitude of the pulling force is given by the following relation;
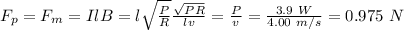
The pulling force
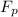 = 0.975 N.
= 0.975 N.