Answer: 0.887 g of
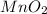 should be added to excess HCl(aq).
should be added to excess HCl(aq).
Step-by-step explanation:
According to ideal gas equation:
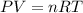
P = pressure of gas = 805 torr = 1.06 atm (760torr=1atm)
V = Volume of gas = 235 ml = 0.235 L
n = number of moles = ?
R = gas constant =
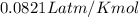
T =temperature =
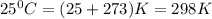
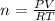
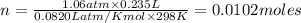
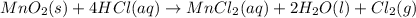
According to stoichiometry:
1 mole of chlorine is produced by = 1 mole of
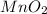
Thus 0.0102 moles of chlorine is produced by =
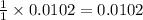 moles of
moles of
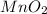
Mass of
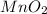 =
=
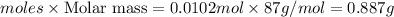
0.887 g of
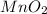 should be added to excess HCl(aq).
should be added to excess HCl(aq).