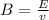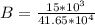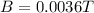Answer:
The magnetic field required required for the beam not to be deflected is
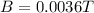
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The charge on the particle is
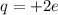
The mass of the particle is
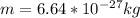
The potential difference is
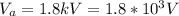
The potential difference between the two parallel plate is
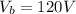
The separation between the plate is
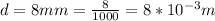
The Kinetic energy experienced by the beam before entering the region of the parallel plate is equivalent to the potential energy of the beam after the region having a potential difference of 1.8kV
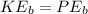
Generelly
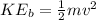
And
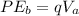
Equating this two formulas
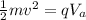
making v the subject
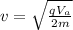
Substituting value

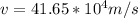
Generally the electric field between the plates is mathematically represented as
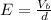
Substituting value
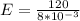
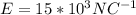
the magnetic field is mathematically evaluate