Answer:
The reaction will be slower because the leaving group will be poorer.
Step-by-step explanation:
The given reaction is an example of
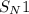 reaction.
reaction.
In the first step, bromide ion leaves the molecule to produce a carbocation. This is the rate determining step.
In the second step, methanol attacks the carbocation to form product of the reaction. This is a fast step and does not have influence on rate of reaction.
Therefore, if we replace Br with Cl then formation of carbocation will require more activation energy as
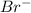 is a better leaving group than
is a better leaving group than
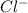 due to higher polarizability of
due to higher polarizability of
Hence, the reaction will be slower when the alkyl halide is changed to 2-chloro-3-methylbutane.