Answer:
In this case, as the null hypothesis is not rejected, the only error possible is Type II error. That means that the researchers conclude that the students are not fluent when they really are fluent in English.
Explanation:
They test an hypothesis to test the claim that students are strong in english.
The null and alternative hypothesis are:
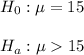
If they reject the null hypothesis, that means that the studens are fluent in English.
With the data they have, they conclude that the evidence is not strong enough to conclude that the students are fluent in English.
That means they failed to reject the null hypothesis.
The type of errors are:
Type I error: reject a true null hypothesis.
Type II error: failed to reject a false null hypothesis.
In this case, as the null hypothesis is not rejected, the only error possible is Type II error. That means that the researchers conclude that the students are not fluent when they really are fluent in English.