Answer:
ΔG° of reaction = -47.3 x
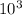 J/mol
J/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
As we can see, we have been a particular reaction and Energy values as well.
ΔG° of reaction = -30.5 kJ/mol
Temperature = 37°C.
And we have to calculat the ΔG° of reaction in the biological cell which contains ATP, ADP and HPO4-2:
The first step is to calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction:
Equilibrium Constant K =
![([HPO4-2] x [ADP])/(ATP)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/g34zyx0zezodfn5v6ucd6r7wxxlvci5aso.png)
And we have values given for these quantities in the biological cell:
[HP04-2] = 2.1 x
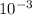 M
M
[ATP] = 1.2 x
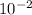 M
M
[ADP] = 8.4 x
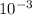 M
M
Let's plug in these values in the above equation for equilibrium constant:
K =
![([2.1x10^(-3)] x [8.4x10^(-3)] )/([1.2 x 10^(-2)] )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/dyoxwfv8yfc2jdgobdwxa45yqmqcrcf1mn.png)
K = 1.47 x
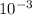 M
M
Now, we have to calculate the ΔG° of reaction for the biological cell:
But first we have to convert the temperature in Kelvin scale.
Temp = 37°C
Temp = 37 + 273
Temp = 310 K
ΔG° of reaction = (-30.5
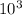 ) + (8.314)x (310K)xln(0.00147)
) + (8.314)x (310K)xln(0.00147)
Where 8.314 = value of Gas Constant
ΔG° of reaction = (-30.5 x
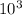 ) + (-16810.68)
) + (-16810.68)
ΔG° of reaction = -47.3 x
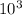 J/mol
J/mol