Answer:
a. The volume V₁ and V₂
b. The case that involves the greatest momentum change = Case B
c. The case that involves the greatest impulse = Case B
d. b. The case that involves the greatest force = Case B
Step-by-step explanation:
Here we have
Case A: V₁ = 150-mL, v₁ = 8 m/s
Case B: V₂ = 600-mL, v₁ = 8 m/s
a. The variable that is different for the two cases is the volume V₁ and V₂
b. The momentum change is by the following relation;
ΔM₁ = Mass, m × Δv₁
The mass of the balloon are;
Δv₁ = Change in velocity = Final velocity - Initial velocity
Mass = Density × Volume
Density of water = 0.997 g/mL
Case A, mass = 150 × 0.997 = 149.55 g
Case B, mass = 600 × 0.997 = 598.2 g
The momentum change is;
Case A: Mass, m × Δv₁ = 149.55 g/1000 × 8 m/s = 1.1964 g·m/s
Case B: Mass, m × Δv₁ = 598.2/1000 × 8 = 4.7856 g·m/s
Therefore Case B has the greatest momentum change
The case that has the gretest momentum change = Case B
c. The momentum change = impulse therefore Case B involves the greatest impulse
d. Here we have;
Impulse = Momentum change =
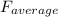 × Δt = mΔV
× Δt = mΔV
∴
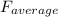 = m·ΔV/Δt
= m·ΔV/Δt
∴ For Case A
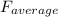 = 149.55×8/Δt = 1196.4/Δt N
= 149.55×8/Δt = 1196.4/Δt N
For Case B
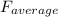 = 598.2×8/Δt = 4785.6/Δt
= 598.2×8/Δt = 4785.6/Δt
Where Δt is the same for Case A and Case B,
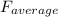 for Case B >>
for Case B >>
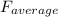 for Case B
for Case B
Therefore, Case B involves the greatest force.