Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The pressure of a gaseous mixture is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the individual gases:
Σ
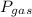
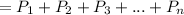
The prompt is trying to confuse you, but it actually tells us the pressure of the mixture to be 1 atm, but this can be converted to torr. Furthermore, we are informed only three gases are in the mixture: diatomic nitrogen, diatomic oxygen, and carbon dioxide:
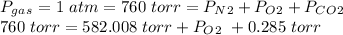
Solve for Po2:
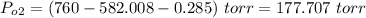
Thus, the partial pressure of diatomic oxygen is 177.707 torr.
If you liked this solution, hit Thanks or give a Rating!