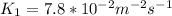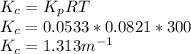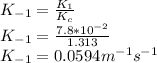Answer:
a)
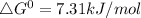
b)
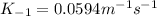
Step-by-step explanation:
Equation of reaction:
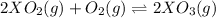
Initial pressure 3 1 0
Pressure change 2P 1P 2P
Total pressure = (3-2P) + (1-P) + (2P)
Total Pressure = 3.75 atm
(3-2P) + (1-P) + (2P) = 3.75
4 - P = 3.75
P = 4 - 3.75
P = 0.25 atm
Let us calculate the pressure of each of the components of the reaction:
Pressure of XO2 = 3 - 2P = 3 - 2(0.25)
Pressure of XO2 =2.5 atm
Pressure of O2 = 1 - P = 1 -0.25
Pressure of O2 = 0.75 atm
Pressure of XO3 = 2P = 2 * 0.25
Pressure of XO3 = 0.5 atm
From the reaction, equilibrium constant can be calculated using the formula:
![K_(p) = ([PXO_(3)] ^(2) )/([PXO_(2)] ^(2)[PO_(2)] )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/qpuhfz86ctf061nmjvspb3fcgkak3sncoy.png)
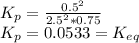
Standard free energy:
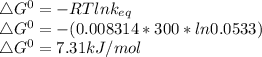
b) value of k−1 at 27 °C, i.e. 300K