Answer:
See the answer and explanation below.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hemophilia is sex linked. Traits that are sex linked are found on the sex chromosomes. For a man, the sex chromosome if XY and for a woma, the sex chromosome if XX. The Y chromosome in man is hypothesized not to carry any gene and hence, a man only need one allele of sex-linked traits in order to be affected while a woman would need two. Also, it means that a man cannot be heterozygous.
For hemophilia:
An affected male will have the genotype:
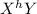
Heterozygous female will have the genotype:
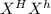
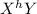 x
x
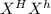
progeny:
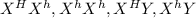 (See the attached image for the Punnet's square).
(See the attached image for the Punnet's square).
Genotype and phenotype
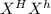 = Physically normal
= Physically normal
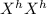 = Hemophilic
= Hemophilic
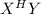 = Physically normal
= Physically normal
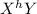 = Hemophilic
= Hemophilic
From the resulting progeny, 2 out of 4 are hemophilic. Hence the likelihood of having a sick child is 2/4 which is equal to 1/2 or 50%.