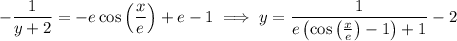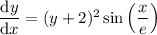
a. If
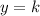 , then
, then
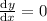 , so
, so
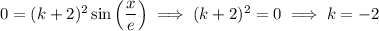
b. When
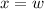 , we're told
, we're told
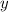 has a horizontal tangent, which has slope
has a horizontal tangent, which has slope
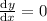 . So we have
. So we have
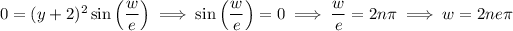
where
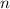 is any integer, whose smallest positive value occurs for
is any integer, whose smallest positive value occurs for
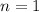 , giving
, giving
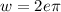 .
.
c. The equation is separable:
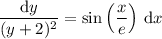
Integrate both sides to get
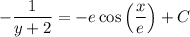
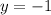 when
when
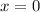 , so we find
, so we find

Then the particular solution to the DE is