From the listed choices, you can prove the series diverges using either the integral or p-series test.
We have
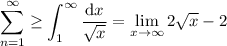
which diverges to infinity, so the series is divergent.
The series
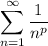
converges only for
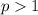 . In the given sum, we have
. In the given sum, we have
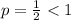 , so the series is divergent.
, so the series is divergent.