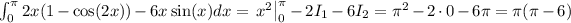Answer:
The answer is
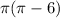
Explanation:
Recall that green theorem is as follows: Given a field F(x,y) = (P(x,y),Q(x,y)) and a closed curve C that is counterclockwise oriented. If P and Q are continuosly differentiable, then
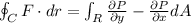
where R is the region enclosed by the curve C.
In this particular case, we have the following field
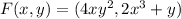 . We are given the description of the region R as
. We are given the description of the region R as
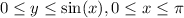 . So, in this case (calculations are omitted)
. So, in this case (calculations are omitted)
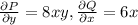
Thus,
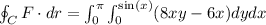
So,
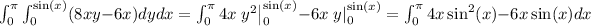
Since
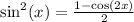 , then
, then
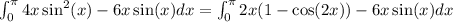
Consider the integrals
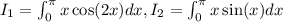
Then, by using integration by parts (whose calculations are omitted) we get
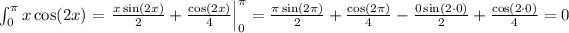
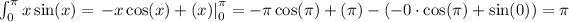
Then, we have that