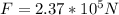Answer:
The force exerted on the roof is
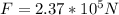
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The speed of the wind is
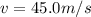
The area of the roof is
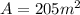
The air density of Boulder is
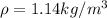
The atmospheric pressure is
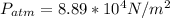
For a laminar flow the Bernoulli’s principle is mathematically represented as
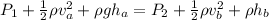
Where
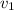 is the speed of air in the building
is the speed of air in the building
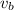 is the speed of air outside the building
is the speed of air outside the building
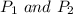 are the pressure of inside and outside the house
are the pressure of inside and outside the house
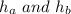 are the height above and below the roof
are the height above and below the roof
Now for
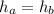
The above equation becomes
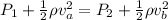
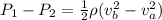
Since pressure is mathematically represented as
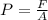
The above equation can be written as
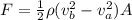
The initial velocity is 0
Substituting value
](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/41kliq69w4zkd5acvivlxzqwc047fxehsd.png)