Answer:
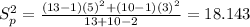
And the deviation would be just the square root of the variance:
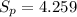
Then the statistic is given by:
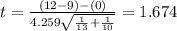
And the correct option would be:
t = 1.674
Explanation:
Data given:
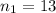 represent the sample size for group 1
represent the sample size for group 1
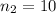 represent the sample size for group 2
represent the sample size for group 2
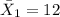 represent the sample mean for the group 1
represent the sample mean for the group 1
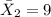 represent the sample mean for the group 2
represent the sample mean for the group 2
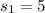 represent the sample standard deviation for group 1
represent the sample standard deviation for group 1
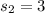 represent the sample standard deviation for group 2
represent the sample standard deviation for group 2
We are assuming two independent samples from two normal distributions with equal variances we are assuming that
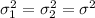
And the statistic is given by this formula:
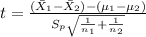
Where t follows a t distribution with
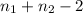 degrees of freedom and the pooled variance
degrees of freedom and the pooled variance
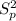 is given by this formula:
is given by this formula:
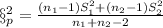
The system of hypothesis on this case are:
Null hypothesis:
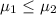
Alternative hypothesis:
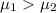
The pooled variance is given by:
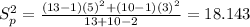
And the deviation would be just the square root of the variance:
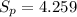
Then the statistic is given by:
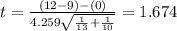
And the correct option would be:
t = 1.674