Answer:
The answer is 1.5 moles.
Step-by-step explanation:
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas that is considered to be composed of point particles that move randomly and do not interact with each other. Gases in general are ideal when they are at high temperatures and low pressures.
An ideal gas is characterized by three state variables: absolute pressure (P), volume (V), and absolute temperature (T). The relationship between them constitutes the ideal gas law:
P * V = n * R * T
where n is the number of moles and R is the molar constant of the gases.
In this case:
- R= 0.082
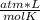
Replacing:
1 atm*33.6 L= n* 0.082
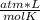 *273 °K
*273 °K
Solving:
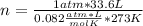
n= 1.5 moles
So, the answer is 1.5 moles.