Answer:
The volume of the gas when pressure decreases to 620 mmHg is 2.52 L
Step-by-step explanation:
Boyle's law is a law related to gases that establish a relationship between the pressure and the volume of a given amount of gas, without variations in temperature, that is, at constant temperature. So, this law establishes that at constant temperature, the volume of a fixed mass of gas is inversely proportional to the pressure it exerts.
Boyle's law is expressed mathematically as:
Pressure * Volume = constant
o P * V = k
Having a certain volume of gas V1 that is at a pressure P1 at the beginning of the experiment, if you vary the volume of gas to a new value V2, then the pressure will change to P2, and it will be true:
P1 * V1 = P2 * V2
In this case:
- P1: 780 mmHg
- V1: 2 L
- P2: 620 mmHg
- V2: ?
Replacing:
780 mmHg* 2 L= 620 mmHg* V2
Solving:
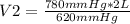
V2= 2.52 L
The volume of the gas when pressure decreases to 620 mmHg is 2.52 L