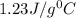Answer: The specific heat of alloy is
Step-by-step explanation:
The quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius is called the specific heat capacity.
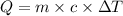
Q = Heat absorbed = 297 J
m= mass of substance = 15.4 g
c = specific heat capacity = ?
Initial temperature =
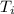 = 5.0°C
= 5.0°C
Final temperature =
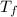 =20.7°C
=20.7°C
Change in temperature ,
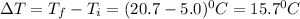
Putting in the values, we get:
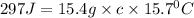
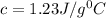
The specific heat of alloy is