Answer : The oxygen will appears in the final chemical equation as a reactant.
Explanation :
The given chemical reactions are:
(1)
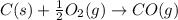
(2)
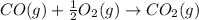
Now we are adding reaction 1 and reaction 2, we get the final chemical equation.
The final chemical equation is:
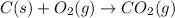
Thus, the oxygen will appears in the final chemical equation as a reactant.