Answer:
18.5 grams
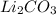
Step-by-step explanation:
First, we'll need to balance the equation:
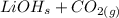 →
→
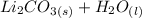
There is one (Li) on the left and two on the right, so let's add a 2 coefficient on the left.
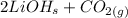 →
→
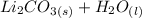
Now there are 2 (Li) on the left, and 2 on the right, 4 (O) on both sides, 1 (C) on both sides, and 2 (H) on both sides. The equation is balanced!
Step 1: Find the limiting reactant
To find the limiting reactant, we need to convert the given masses of each reactant into moles. Multiply the given masses by the molar masses.
12g 2LiOh ×
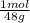 (double the molar mass because you have two molecules) = 0.25 moles
(double the molar mass because you have two molecules) = 0.25 moles
12g CO₂ ×
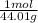 = 0.272 moles
= 0.272 moles
We'll test both reactants to see which one limits us.
- Given 0.25 mole LiOH ×
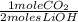 = .125 moles CO₂ needed
= .125 moles CO₂ needed - Given 0.272 moles CO₂ x
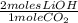 = 0.545 moles LiOH needed
= 0.545 moles LiOH needed
Since we don't have enough CO₂ to use all of our LiOH, CO₂ is the limiting reactant. We will use all of the CO₂ to perform our reaction and ignore the excess LiOH.
Step 2: Calculating the mass of the product
You can find the mass of either product with a mole ratio. (Remember, we have too much CO₂, so we'll need to use the given LiOH to perform this calculation)
0.25 moles LiOH ×
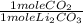 = 0.25 moles
= 0.25 moles
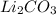
Now we convert back to grams!
0.25 moles
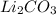 ×
×
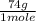 = 18.5 grams
= 18.5 grams