Answer:
There are 0.925 moles of nickel (II) chloride present in the final 1 L volume solution.
Step-by-step explanation:
The solutions are homogeneous mixtures (that is to say that their properties and composition are uniform) of two or more substances. We call the substance in the highest proportion: solvent, and the substance or substances in the smallest proportion: solute.
Molarity describes the relationship between the moles of a solute and the volume of a solution. Then, the molarity is equal to the number of moles of a solute divided by the volume of the solution in liters:
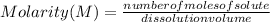
Molarity is expressed in units (
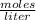 ).
).
If the solution has a molarity of 0.925, it indicates that there are 0.925 moles of nickel (II) chloride present in the final 1 L volume solution.