Answer:
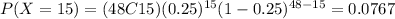
And that would be the exact answer
Since the problem states that we need to use the normal approximation for the binomial distribution we can find the mean and the expected value with:
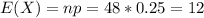
And the standard deviation:
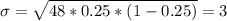
But the problem is that if we assume that the distribution is continuous then we can find the probability for an exact value since the probability for a single value in continuous distributions is 0 since the area below a line is 0.
Explanation:
For this case we degine the random variable X a the number of correct answers in 48 trials, and for this case the distirbution for X would be:
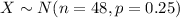
The probability mass function for the Binomial distribution is given as:
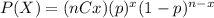
Where (nCx) means combinatory and it's given by this formula:
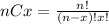
And using this we can find the required probability as:
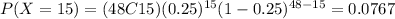
And that would be the exact answer
Since the problem states that we need to use the normal approximation for the binomial distribution we can find the mean and the expected value with:
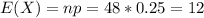
And the standard deviation:
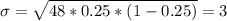
But the problem is that if we assume that the distribution is continuous then we can find the probability for an exact value since the probability for a single value in continuous distributions is 0 since the area below a line is 0.