Answer:
For 1: The molecular equation is
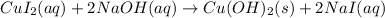
For 2: The net ionic equation is
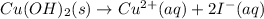
For 3: The equilibrium constant expression is
![K_(eq)=[Cu^(2+)][I^-]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/x1ijxpofvb6ruj1mjkq0k1e804b3e3ty4f.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
A molecular equation is defined as the chemical equation in which the ionic compounds are written as molecules rather than component ions.
The molecular equation for the reaction of copper (II) iodide and sodium hydroxide is given as:
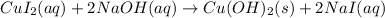
Net ionic equation of any reaction does not include any spectator ions.
Spectator ions are defined as the ions which does not get involved in a chemical equation. They are found on both the sides of the chemical reaction when it is present in ionic form.
The chemical equation for the reaction of copper hydroxide and sodium iodide is given as:
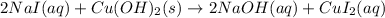
Ionic form of the above equation follows:
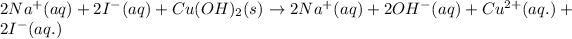
As, sodium and iodide ions are present on both the sides of the reaction. Thus, it will not be present in the net ionic equation and are spectator ions.
The net ionic equation for the above reaction follows:
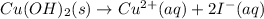
The expression of equilibrium constant for the net ionic equation above follows:
![K_(eq)=[Cu^(2+)][I^-]^2](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/x1ijxpofvb6ruj1mjkq0k1e804b3e3ty4f.png)
Concentrations of pure solids and pure liquids are taken as 1 in equilibrium constant expression.