Answer:
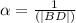 , (plug in the value of BD to get the answer, you did not provide it in your question)
, (plug in the value of BD to get the answer, you did not provide it in your question)
Step-by-step explanation:
Absolute acceleration of point B,
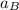 = 4 m/s²
= 4 m/s²
Absolute acceleration for point D,
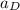 = 3 m/s²
= 3 m/s²
Acceleration of point B relative to D in the normal direction BD,
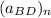 = 0 (the cable moves with constant velocity)
= 0 (the cable moves with constant velocity)
Acceleration of point B relative to D in the tangential direction to BD,
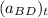 = ?
= ?
The equation for the relative acceleration for the motion between B and D:
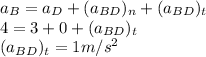
To determine the angular acceleration of the beam
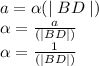
Note: You did not provide the value for the distance between B and D, this value is needed to calculate the angular acceleration. Plug in the value for BD and get your answer