Answer:
Neither of them will neutralize the buffer solution.
Step-by-step explanation:
The buffer solution of HNO₂ and KNO₂ will be neutralized when the acid reacts and consume all of the base of the buffer solution or when the base added reacts and consume all of the acid of the buffer solution.
First, we need to calculate the number of moles of the acid and the base of the buffer:
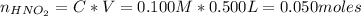
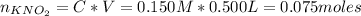
Now, let's evaluate each case.
A) 250 mg of NaOH:
We need to calculate the number of moles of NaOH
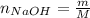
Where m: is the mass = 250 mg, and M: is the molar mass = 39.99 g/mol
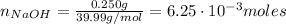
The number of moles of the acid HNO₂ after reaction with the base added NaOH is:
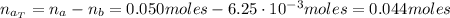
After the reaction of HNO₂ with the NaOH remains 0.044 moles of acid, hence, 250 mg of NaOH would not exceed the capacity of the buffer to neutralize it.
B) 350 mg KOH:
The number of moles of KOH is:
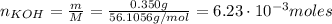
Now, the number of moles of HNO₂ that remains in the solution is:
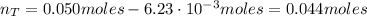
Therefore, 350 mg of KOH would not exceed the capacity of the buffer to neutralize it.
C) 1.25 g of HBr:
The number of moles of HBr is:
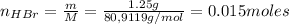
Now, the number of moles of the base KNO₂ that remains in solution after the reaction with HBr is:
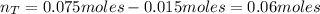
Hence, 1.25 g of HBr would not exceed the capacity of the buffer to neutralize it.
D) 1.35 g of HI:
The number of moles of HI is:
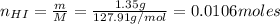
Now, the number of moles of the base KNO₂ that remains in solution after the reaction with HI is:
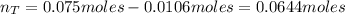
Hence, 1.35 g of HI would not exceed the capacity of the buffer to neutralize it.
Therefore, neither of them will neutralize the buffer solution.
I hope it helps you!