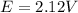Complete Question
The overall reaction in the lead storage battery is
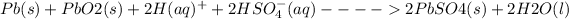
Calculate E at 25°C for this battery when [H2SO4] = 5.0 M; that is, [H + ] = [HSO4− ] = 5.0 M. At 25°C, E° = 2.04 V for the lead storage battery.
Answer:
The voltage of the cell is
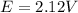
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The original voltage of the battery is
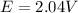
The concentration of [H2SO4] = 5.0 M
The concentration of [H + ] = [HSO4− ] = 5.0 M
At equilibrium
The reaction quotient is
![Q = (1)/([[HSO_4^-]^2 [H^+] ^2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/68kmu8m1jc48v97gq7gwqjakhm2hq97egu.png)
Pb(s), Pb(s), 2 H2O(l),2 PbSO4(s) are excluded from the reaction above because they are solid and liquid thus there concentration does not change
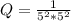

So the potential for the battery cell is mathematically evaluated as
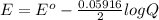
![= 2.04 - [(0.05916)/(2) log (1.6*10^(-3))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/by76cbhz7xkuvkr5l7xtvowlk6a1z96cat.png)