Answer:
(a) The electron will move towards the wire.
The direction of the magnetic fields created by the wire can be found via right-hand rule. If you point your thumb towards the direction of the current, and if you curl your fingers, the direction of your four fingers will give the direction of the magnetic field. In this case, magnetic field is around the wire, and into the page just above the wire, where the electron is located.
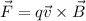
According to the above formula, the direction of the force the wire applies to the electron can be found by right-hand rule.
Since the electron has a negative charge, the direction of the force is towards the wire.
(b) The proton will veer to the right.
The direction of the magnetic field is the same as the previous part. The proton has a positive charge, and coming from above. The direction of its velocity is downwards. The magnetic field above the wire is pointed into the page. Using the right-hand rule, the magnetic force on the proton is directed to the right, with respect to us.