Answer:
a) the longest wavelength of the light that will eject electrons from the silicon surface is 258.7891 nm
b) maximum kinetic energy will electrons reach the anode is 0.5098 eV
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Wavelength range = 141-295 nm
Potential of 3.5 V
For the silicon, the work function is Φ = 4.8 eV = 7.68x10⁻¹⁹J
Questions:
a) What is the longest wavelength of the light that will eject electrons from the silicon surface, λ = ?
b) With what maximum kinetic energy will electrons reach the anode,
a) The longest wavelength that will eject electrons:
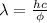
Here
h = Planck's constant = 6.625x10⁻³⁴J s
c = speed of light = 3x10⁸m/s
Substituting values:
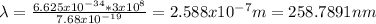
b) The maximum kinetic energy (one electron):
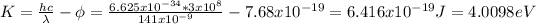
Now, you need to calculate the potential difference:
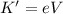
Here
e = charge of electron = 1.6x10⁻¹⁹C
Substituting:
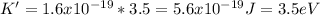
Now, the maximum kinetic energy of the electrons:
Kmax = 4.0098 - 3.5 = 0.5098 eV