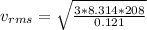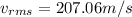Answer:
The root mean squared velocity for CF2Cl2 is
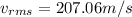
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The temperature is
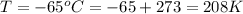
Root Mean Square velocity is mathematically represented as
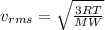
Where T is the temperature
MW is the molecular weight of gas
R is the gas constant with a value of
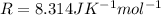
For CF2Cl2 its molecular weight is 0.121 kg/mol
Substituting values