Answer:
There are needed 5.28*10⁵ photons.
Step-by-step explanation:
The energy of a photon of wavelength 500 nm can be calculated from the formula:
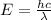
Where E is the energy of the photon, h is the Planck's constant and c is the speed of light in vacuum.
Next, since we are comparing this energy with the energy of a gamma-ray photon, we can say that this energy multiplied by the number of photons should be equal to the energy of gamma-ray photon:
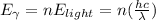
And solving for the number of photons, we get:
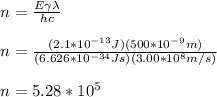
So, there are needed 5.28*10⁵ visible-light photons of wavelength 500nm to match the energy of a single gamma-ray photon with energy 2.1*10⁻¹³J.