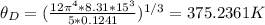Answer:
The Debye temperature for aluminum is 375.2361 K
Step-by-step explanation:
Molecular weight of aluminum=26.98 g/mol
T=15 K
The mathematical equation for the specific heat and the absolute temperature is:
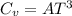
Substituting in the expression of the question:
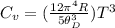
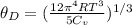
Here
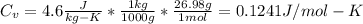
Replacing: