Answer:
0.407 m
Step-by-step explanation:
T = Time period = 0.6 s
A = Amplitude = 27 cm
m = Mass = 120 g
Angular speed is given by
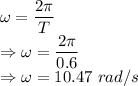
Spring constant is given by
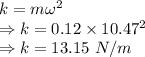
As the energy of the system is conserved we have
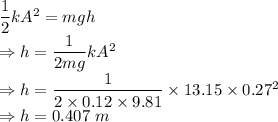
The animal will go 0.407 m above its equilibrium position.