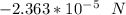Answer:
The magnitude of the force F =
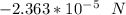
The direction of the force is in opposite direction.
Step-by-step explanation:
The expression for force per unit length between two parallel wires carrying current
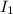 and
and
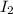 can be written as:
can be written as:
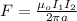
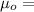 permeability constant =
permeability constant =
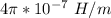
a = distance between the wires = 4.00 cm = 0.04 cm
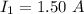
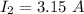
replacing our values into the above equation; we have:
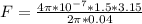
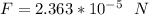
Hence, If the current flows in the same direction, then , the force is said to be attractive (+ve) . However, if the direction of the current flow is opposite; then the force is said to be repulsive (-ve).
From the question given, the current flows in opposite direction in the wires, thus the force is said to be repulsive.
Thus ; F =