Answer:
0.057258
Explanation:
From the statement of the problem, the following information were given:
- P(Positive|HIV)=0.979
- P(Negative|No HIV)=0.919
- P(HIV)=0.005
The following can be derived:
- P(Positive|No HIV)=1-P(Negative|No HIV)=1-0.919=0.081
- P(No HIV)=1-P(HIV)=1-0.005=0.995
We are to determine the probability that a person has HIV given that they test positive. [P(HIV|Positive)]
Using Baye's theorem for Conditional Probability
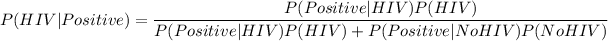
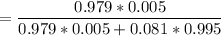
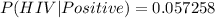
The probability that a random person tested has HIV given that they tested positive is 0.057258.