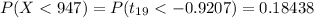Answer:
a) P(Xs<947)=0.1844
b) The sampling distribution has to be evaluated with the t-students distribution, as the population standard deviation is not known.
Explanation:
We have a sample of n=20 weather stations, with a sample average lifetime of 947 days and a sample standard deviation of s=136 days.
The population mean lifetime is 975 days.
We have to calculate the probability of having a sample with mean of 947 days or less, given that the population mean is 975 days.
As the population standard deviation is unknown, we will use the t-value and estimate the population standard deviation with the sample standard deviation.
The t-value for a X=947 is:
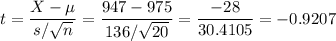
The degrees of freedom are:
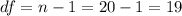
We can now calculate the probability of having a sample with mean of 947 days or less: