Answer: a)
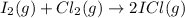 : too close to decide.
: too close to decide.
b)
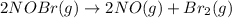 :
:
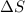 > 0.
> 0.
c)
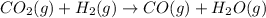 : too close to decide.
: too close to decide.
d)
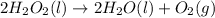 :
:
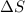 > 0.
> 0.
Step-by-step explanation:
Entropy is the measure of randomness or disorder of a system. If a system moves from an ordered arrangement to a disordered arrangement, the entropy is said to decrease and vice versa.
For the reaction:
a)
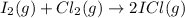
In this reaction 2 moles of gaseous reactants are converting to 2 moles of gaseous products. Thus
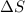 is too close to decide.
is too close to decide.
b)
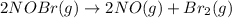
In this reaction 2 moles gaseous reactants is getting converted to 3 moles of gaseous products. Thus the randomness will increase and hence entropy will also increase.Thus
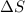 > 0.
> 0.
c)
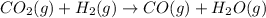
In this reaction 2 moles of gaseous reactants are converting to 2 moles of gaseous products. Thus
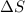 is too close to decide.
is too close to decide.
d)
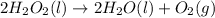
In this reaction 2 moles liquid reactants is getting converted to 2 moles of liquid and 1 mole of gaseous products. Thus the randomness will increase and hence entropy will also increase.Thus
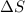 > 0.
> 0.