Answer:
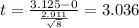
We can use the p value as a decision rule is
 we reject the null hypothesis.
we reject the null hypothesis.
Now we can find the degrees of freedom given by:
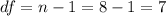
And the p value would be:
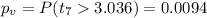
And since the
 we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis in favor to the alternative hypothesis.
we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis in favor to the alternative hypothesis.
Explanation:
For this case we have the following statistics for the difference between the paired observations:
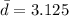 the sample mean for the paired difference
the sample mean for the paired difference
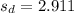 the sample deviation for the paired difference data
the sample deviation for the paired difference data
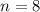 the sample size
the sample size
The system of hypothesis that we want to check is:
Null hypothesis:
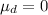
Alternative hypothesis:
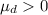
And the statistic is given by:
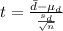
And replacing we got:
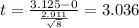
We can use the p value as a decision rule is
 we reject the null hypothesis.
we reject the null hypothesis.
Now we can find the degrees of freedom given by:
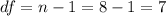
And the p value would be:
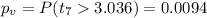
And since the
 we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis in favor to the alternative hypothesis.
we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis in favor to the alternative hypothesis.