Answer:
Null Hypothesis,
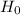 :
:
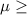 21 miles per gallon
21 miles per gallon
Alternate Hypothesis,
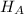 :
:
 < 21 miles per gallon
< 21 miles per gallon
Explanation:
We are given that a car company says that the mean gas mileage for its luxury sedan is at least 21 miles per gallon (mpg).
You believe the claim is incorrect and find that a random sample of 8 cars has a mean gas mileage of 19 mpg and a standard deviation of 3 mpg.
Let
 = mean gas mileage for its luxury sedan
= mean gas mileage for its luxury sedan
So, Null Hypothesis,
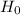 :
:
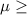 21 miles per gallon
21 miles per gallon
Alternate Hypothesis,
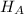 :
:
 < 21 miles per gallon
< 21 miles per gallon
Here, null hypothesis states that the mean gas mileage for its luxury sedan is at least 21 miles per gallon (mpg).
On the other hand, alternate hypothesis states that the mean gas mileage for its luxury sedan is less than 21 miles per gallon (mpg).
The test statistics that would be used here is One-sample t test statistics as we don't know about population standard deviation i.e;
T.S. =
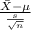 ~
~
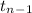
Hence, the above hypothesis is appropriate for the given situation.