Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
This question is based on oscillation in spring - mass system
time period is given by the relation T = 2π
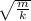
m is mass attached , k is spring constant of spring .
In the first case
mass m = 36.4 kg , T = 1.4
Putting these values in the equation above
1.4 = 2π
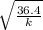
1.4² = 4π² x
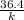
k = 732.42 N / m
In the second case
mass m = (36.4+m ) kg , T = 2.22s , m is mass of astronaut
Putting these values in the equation above
2.22 = 2π
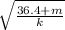
2.22² = 4π² x
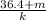
Putting the value of k
2.22² = 4π² x
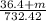
36.4 + m = 91.53
m = 55.12.kg