Answer:
-185.75297
Explanation:
Solution:-
- We are testing whether the population mean u is equal to 100 as per claim.
Null hypothesis: u = 100
- Where a alternate hypothesis suggest that the population mean ( u ) may be lower:
Alternate hypothesis: u < 100
- We are given sample data parameters which are assumed to be normally distributed:
sample mean, x_bar = 9
sample standard deviation, s = 2.4
- A sample of n = 24 observation was taken from a population of ( N ) with unknown population standard deviation ( σ ).
- The conditions of standard normal distribution are no longer applicable i.e:
n = 24 < 30
unknown population standard deviation ( σ )
- We will model the sample using t-distribution with ( n - 1 ) = 23 degrees of freedom.
- The t-statistics of the sample mean x_bar can be determined from standard t-distribution:
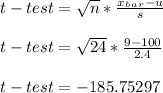
- The t-test value for mean ( u ) is -185.75297