Answer:
1/4
Step-by-step explanation:
The probability of having a son with normal phenotype would be 1/4.
Both color blindness and anemia are X-linked and are linked together. The genes for X-linked disorders are found on the sex chromosomes with the male being XY and female being XX. The male child gets his X chromosome from the mother and Y from the father while the female child gets one of her X chromosome form the father and the other from the mother.
For recessive disorders, two recessive alleles are needed by the female on the two X chromosome to become affected while only one allele is needed on one X chromosome of the male to become affected.
Assuming the allele for color blindness is a and that of anemia is b.
George is color blind but not anemic, the genotype would be
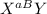
Martha is normal but her dad is color blind and anemic, this means that Martha is a carrier for both disorders with genotype
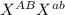
Crossing the two genotypes
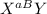 x
x
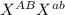
offspring:
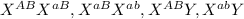
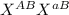 = normal phenotype female
= normal phenotype female
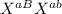 = color blind, non anemic female
= color blind, non anemic female
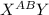 = normal phenotype male
= normal phenotype male
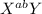 = color blind, anemic male
= color blind, anemic male
Probability of having a son = 1/2
Probability of producing a normal phenotype child = 1/2
Hence,
Probability of a son with normal phenotype = 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4.