Answer:
The H2 gas occupies the length of x = 111.94 cm of the cylinder while N2 gas occupies the length of L - x = 120 - 111.94 = 8.055 cm
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:-
- The length of the cylinder, L = 120 cm
- The mass of the N2 = mn
- The molecular mass of N2, Mn = 28.013 g / mol
- The molecular mass of H2, Mh = 2.016 g / mol
- The mass of the H2 = mh.
- The universal gas constant = Ru
FInd:-
Where is the piston located when one side is filled with nitrogen N2 and the other side with the same mass of hydrogen H2 at the same temperature?
Solution:-
- We will assume both gases ( N2 and H2 ) to have ideal behaviour. The ideal gas law is applicable.
- Since ideal gas is defined as one in which all collisions between atoms or molecules are perfectly elastic and in which there are no intermolecular attractive forces.
- In other words, the Ideal Gas Law is accurate only at relatively low pressures (relative to the critical pressure pcr) and high temperatures (relative to the critical temperature Tcr). At these parameters, the compressibility factor, Z = pv / RT, is approximately 1.
- Ideal gas state equation is given below:
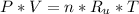
Where,
P : The absolute pressure of the gass
V : The volume occupied by the gas
n : The number of moles of the gas
Ru : The universal ideal gas constant
T : The absolute temperature of gas ( Kelvin )
- The number of moles ( n ) of a gas is defined by the ratio of mass of gas in ( kg ) and the molecular weight of the gas ( Mr ). Given by:
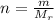
- Substitute the number of moles in the Ideal gas state equation. We have:
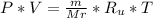
- Now from the data given the pressures, mass and temperatures of the gasses are equal. So we will formulate the two state equation for each gas.
N2:
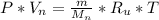
H2:
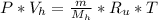
- Divide the state equations for both gases , ( N2 / H2 ):
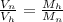
- Use the given data to compute the ratio of volume occupied by the both gasses.
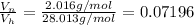
- We will assume the cross-section area "A" of the cylinder does not vary along the length of the cylinder. So for one dimensional length " x " defines the length of the cylinder occupied by the H2 gas.
- The remaining length " L - x " is occupied by the N2 gas then we have:
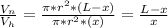
- Now equate the ratio calculated:
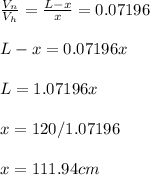
- The H2 gas occupies the length of x = 111.94 cm of the cylinder while N2 gas occupies the length of L - x = 120 - 111.94 = 8.055 cm