Answer:
The volume that 454.5 grams of gaseous hydrogen will occupy at 1,050 atm and 25.00 ℃ will be 5,288.65 L
Step-by-step explanation:
An ideal gas is characterized by three state variables: absolute pressure (P), volume (V), and absolute temperature (T). The relationship between them constitutes the ideal gas law, an equation that relates the three variables if the amount of substance, number of moles n, remains constant and where R is the molar constant of the gases:
P * V = n * R * T
In this case it is necessary to know the molar mass to calculate the amount of moles n. The molar mass of H2 is 2 g / mole. Then the following rule of three can be applied: if 2 grams are contained in 1 mole of substance, 454.5 grams in how many moles will they be contained?
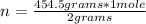
n=227.25 moles
Then, you know:
- R=0.082
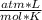
- T=25 °C= 298 °K (0°C=273°K)
Replacing:
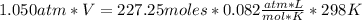
Solving:
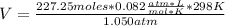
V= 5,288. 65 L
The volume that 454.5 grams of gaseous hydrogen will occupy at 1,050 atm and 25.00 ℃ will be 5,288.65 L