Answer:
7,859.9829 kPa
Step-by-step explanation:
An ideal gas is characterized by three state variables: absolute pressure (P), volume (V), and absolute temperature (T). The relationship between them constitutes the ideal gas law, an equation that relates the three variables where R is the molar constant of the gases:
P * V = n * R * T
Then the pressure can be calculated as:
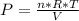 Equation (A)
Equation (A)
In this case R is a known constant and the volume and temperature are given as data. The number of moles n can be calculated from the molar mass. You know:
Then the molar mass of CO₂ is:
CO₂= 12 g/mole + 2*16 g/mole= 44 g/mole
Now you can apply the following rule of three: if 44 g are contained in 1 mole of CO₂, 94.6 g in how many moles are they?
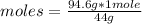
moles= 2.15
Then you know the following data:
- n= 2.15 moles
- R= 0.082
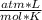
- T= 57 C= 330 K (0 C= 273 K)
- V= 0.75 L
Replacing in Equation (A):
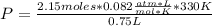
Solving:
P= 77.572 atm
Knowing that 1 atm is equal to 101.325 kPa, then 77.572 atm is 7,859.9829 kPa