Answer: The Gibbs free energy of the reaction is 21.32 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
The chemical equation follows:
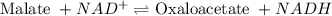
The equation used to Gibbs free energy of the reaction follows:
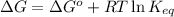
where,
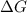 = free energy of the reaction
= free energy of the reaction
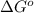 = standard Gibbs free energy = 29.7 kJ/mol = 29700 J/mol (Conversion factor: 1 kJ = 1000 J)
= standard Gibbs free energy = 29.7 kJ/mol = 29700 J/mol (Conversion factor: 1 kJ = 1000 J)
R = Gas constant = 8.314J/K mol
T = Temperature =
![37^oC=[273+37]K=310K](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/moa8yolmutetgaufwr1a897os3p5970uma.png)
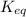 = Ratio of concentration of products and reactants =
= Ratio of concentration of products and reactants =
![\frac{\text{[Oxaloacetate]}[NADH]}{\text{[Malate]}[NAD^+]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/73i4knhx7xsun74d14nfmiuu20d7igprba.png)
![\text{[Oxaloacetate]}=0.130mM](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/huqo1q34gaokqwf9jw1v0gc2bg2y4x292r.png)
![[NADH]=2.0* 10^2mM](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/g0bvl9ohdt4dwu43oxiqxonmrjr6e5xyia.png)
![\text{[Malate]}=1.37mM](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/tkjq3lhzzgea2xqlaochngk2omv1evva22.png)
![[NAD^+]=490mM](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/qa5kk5z9ivkvnij995jj7ghxlu39wgrg72.png)
Putting values in above expression, we get:
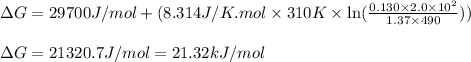
Hence, the Gibbs free energy of the reaction is 21.32 kJ/mol