Answer:
a) 0.142mH
b) 14mV
Step-by-step explanation:
the complete answer is:
(a) Calculate the self-inductance of a solenoid that is <ghtly wound with wire of diameter 0.10 cm, has a cross-sec<onal area of 0.90 cm2 , and is 40 cm long. (b) If the current through the solenoid decreases uniformly from 10 to 0 A in 0.10 s, what is the emf induced between the ends of the solenoid
a) the self inductance of a solenoid is given by:
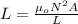
μo: magnetic permeability of vacuum = 4\pi*10^{-7}N/A^2
A: cross sectional area = 0.9cm^2=9*10^{-5}m
L: length of the solenoid = 40cm = 0.4m
The N turns of the wire is calculated by using the diameter of the wire:
N = (40cm)/(0.10cm)=400
By replacing in the formula you obtain:
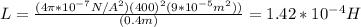
the self inductance is 1.42*10^{-4}H = 0.142mH
b) to find the emf you can use:
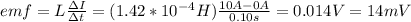
the emf induced is 14mV