Answer: 158 grams
Step-by-step explanation:
As the relative lowering of vapor pressure is directly proportional to the amount of dissolved solute.
The formula for relative lowering of vapor pressure will be,
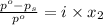
where,
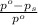 = relative lowering in vapor pressure
= relative lowering in vapor pressure
i = Van'T Hoff factor = 1 (for non electrolytes)
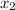 = mole fraction of solute =
= mole fraction of solute =
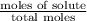
Given : x g of ethylene glycol is present in 183 g of water
moles of solute (ethylene glycol) =
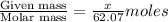
moles of solvent (water) =
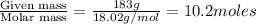
Total moles = moles of solute (ethylene glycol) + moles of solvent (water) =
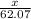 + 10.2
+ 10.2
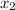 = mole fraction of solute =
= mole fraction of solute =
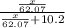
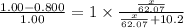
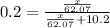
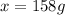
Thus the mass of ethylene glycol should be 158 g