Answer:
Total energy required is J 138883.36 or 138.88336 KJ
Step-by-step explanation:
The total energy required to change 22 g of ice at -20°C, to water, with a temperature of 50°C is:
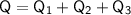
where:
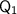 is the energy required to melt the ice.
is the energy required to melt the ice.
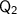 is the energy required to raise the temperature of the water from -20°C to 0°C
is the energy required to raise the temperature of the water from -20°C to 0°C
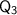 is the energy required to raise the temperature of the water from 0°C to 50°C
is the energy required to raise the temperature of the water from 0°C to 50°C
The energy required to melt the ice is:
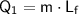
where:
- m is the mass of the ice (22 g)
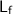 is the latent heat of fusion for ice (6.02 kJ/mol)
is the latent heat of fusion for ice (6.02 kJ/mol)
Now,

The energy required to raise the temperature of the water from -20°C to 0°C is:
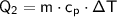
where:
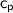 is the heat capacity of water (4.184 J/g-C)
is the heat capacity of water (4.184 J/g-C)
 is the change in temperature (0 - 20 = 20°C)
is the change in temperature (0 - 20 = 20°C)
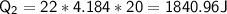
The energy required to raise the temperature of the water from 0°C to 50°C is:
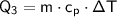
where:
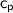 is the heat capacity of water (4.184 J/g-C)
is the heat capacity of water (4.184 J/g-C)
 is the change in temperature (0 - 50 = 50°C)
is the change in temperature (0 - 50 = 50°C)
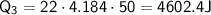
Therefore, the total energy required is:
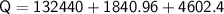
Q=138883.36
So, the answer is Total energy required is 138883.36 J or 138.88336 KJ