Answer:
(a) v = 2.93x10⁶ m/s
(b) T = 1.43x10⁻⁷ s
(c) K = 1.79x10⁵ eV
(d) ΔV = 89.5 kV
Step-by-step explanation:
(a) The speed of the alpha particle can be found using the magnetic force (Fm) and the centripetal force (Fc):
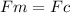
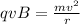
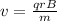 (1)
(1)
Where:
q: is the charge on the alpha particle = 2e⁻ = 2*1.602x10⁻¹⁹ C = 3.20x10⁻¹⁹ C
r: is the radius of the circular path = 6.68 cm = 6.68x10⁻² m
B: is the magnetic field = 0.917 T
m: is the mass of the alpha particle = 4.00 u = 4*1.67x10⁻²⁷ kg = 6.68x10⁻²⁷kg
Hence, the speed of the alpha particle is:
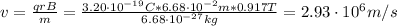
(b) The period (T) of revolution of the alpha particle is:
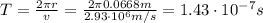
(c) The kinetic energy (K) of the alpha particle is:
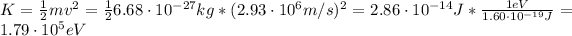
(d) The potential difference (ΔV) is:
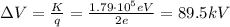
I hope it helps you!