Complete Question:
A survey reported the number of meters (m) per week swam by two groups of swimmers—those who competed exclusively in breaststroke and those who competed in the individual medley (which includes breaststroke). The number of meters per week practicing the breaststroke was recorded for each swimmer, and the summary statistics are given below. Is there sufficient evidence to indicate that the average number of meters per week spent practicing breaststroke is greater for exclusive breaststrokers than it is for those swimming individual medley?
Specialty
Exclusive Breaststroke Individual Medley
Sample size 130 80
Sample mean (m) 9017 5853
Sample standard deviation (m) 7162 1961
Population mean
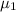
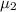
a. State the null and alternative hypothesis
b. What is the appropriate rejection region for an α = 0.01 level test?
c. Calculate the observed value of the appropriate test statistics
d. What is your conclusion?
e. What is a practical reason for the conclusion you reached in pat (d)?
Answer:
c. 4.76
Step-by-step explanation:
from the table shown above
let Y₁ be the number of meters (m) per week swum by those who competed exclusively in the Beast stroke
let Y₂ be the number of meters per week swum by those who competed in the individual medley
a)
Null hypothesis H₀:
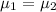
alternative Hypothesis H₁:
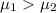 (Right tailed test)
(Right tailed test)
the attached images shows additional details of the solution